Ağız Diş ve Çene Cerrahisi
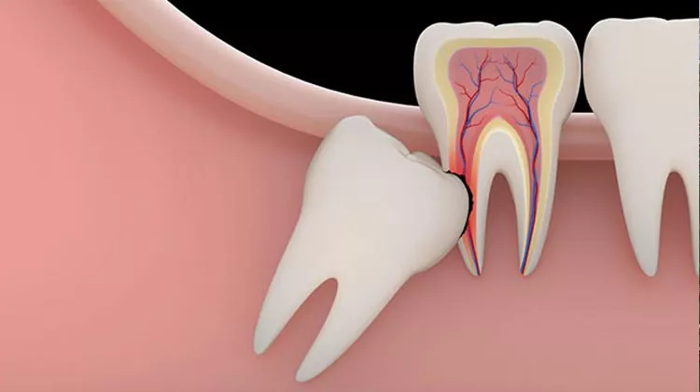
Yirmi yaş dişleri, toplamda 4 adet olmak üzere sıklıkla 16-25 yaşları arasında çıkan üçüncü büyük azı dişleridir. 20’lik dişler olarak adlandırılsa da bazı özel durumlarda çok daha geç yaşta bile sürebilmektedir.
-Yirmi yaş dişleri çıkarken ne gibi sorunlar oluşturur?
Herkesin çene ve diş yapısı aynı olmadığı için bu dişler çıkarken her zaman problem oluşturmazlar. Ancak bazı kişilerde kulaklara ve çeneye yayılan ağrı, diş etinde şişlik, ağız açıklığında kısıtlanma gibi belirtiler verebilir.
-Yirmi yaş dişlerim çıkmadı. Gömülü olup olmadığı nasıl anlaşılır?
Diş hekiminiz sizi muayene edip röntgen aldığında yirmi yaş dişlerinizin oluşup oluşmadığını, dişin pozisyonunu, kendiliğinden çıkıp çıkamayacağını değerlendirir.
-Yirmi yaş dişleri neden gömülü kalır?
Çenelerde en arkada ve en son çıkan bu dişler komşu dişin pozisyonu, üzerlerindeki kemiğin yapısı veya dişeti kalınlığı sebebiyle ağız içinde yeterli yer bulamayabilirler. Bu durumda, kemik veya dişeti altında kısmen veya tamamen gömülü kalırlar.
-Yirmi yaş dişlerinin çekimi zorunlu mudur?
Diş dizisini bozmayacak şekilde sürmüş olan ve alt-üst kapanışta olan yirmi yaş dişlerinin çekilmesine gerek yoktur. Ancak ileri derecede çürük, komşu dişlerde ağrı, kemikte enfeksiyon, kök ucunda kist oluşumu vb. gözlenen 20 yaş dişleri çekilmelidir.
-Yirmi yaş dişlerinin çekimi normal diş çekiminden farklı mıdır?
Ağız içinde görülen yirmi yaş dişlerinin çekiminde diğer diş çekimlerinden bir farklılık yoktur. Ancak gömülü kalan yirmi yaş dişlerinde “cerrahi çekim”(ameliyatla çekim) gerekebilir.
-Diş çekimi sonrası nelere dikkat etmeliyim?
Diş çekimi sonrasında anestezi etkisi geçene kadar gıda tüketmeyin. Ağrı ve şişliğin azalması için ilk 24 saat beşer dakika aralıklarla soğuk kompres(buz) uygulayın. Pıhtılaşmanın bozulmaması ve kanamanın artmaması için ilk 24 saat tükürme, vakumlama, gargara yapmayın. Doktorunuzun yazdığı ilaçları kullanın. Çok sıcak, baharatlı, asitli ve taneli gıdalardan uzak durun. Ağız içinde dikişler olabilir, dikişlerin temiz kalmasına, üzerinde gıda birikmemesine dikkat edin. Dikişlerin zarar görmemesi için aşırı dudak ve dil haraketlerinden kaçının. İyileşme süresince sigara ve alkol tüketmeyin.
-Çekim sonrasında doktora başvurmam gereken acil durumlar nelerdir?
Çekim sonrasında hafif bir yüz şişmesi, sızıntı şeklinde kanama, ağrı kesici aldığında geçen ağrı, ağız açıklığında azalma normaldir. Ancak, tamponlama ile geçmeyen aşırı kanama, birkaç günden fazla süren şişlik, çenelerde uyuşukluk veya karıncalanma hissi varsa mutlaka doktorla iletişime geçilmelidir.
—–İngilizce
-What are the wisdom teeth, when do they develop?
Wisdom teeth are the third molars, which develep frequently between the ages of 16-25, with a total of 4 teeth. Although they usually erupt in the twenties, in some special cases they can erupt even at a much later age.
-What kind of problems does it cause while wisdom teeth are erupting?
Since everyone’s jaw and tooth structure are not the same, these teeth do not always cause problems while they are erupting. However, in some people, it may cause symptoms such as jaw and ear pain, swelling in the gums, and restriction in mouth opening.
-My wisdom teeth are not visible. How to tell if it is impacted?
When your dentist examines you and takes x-rays, he or she evaluates whether your wisdom teeth are formed, the position of the tooth and whether it is impacted.
-Why do wisdom teeth remain impacted?
These teeth, which erupt at the back and last in the jaws, may not find enough space in the mouth due to the position of the adjacent tooth, the structure of the bone or the thickness of the gingiva. In this case, they remain partially or completely impacted in the bone or under the gingiva.
-Is it necessary to remove the wisdom teeth?
It is not necessary to extract the wisdom teeth that have erupted in the right way that does not disrupt the tooth sequence and are in the lower-upper bite. However, if advanced caries, pain in adjacent teeth, infection in the bone, cyst formation at the root, etc. are observed wisdom teeth should be extracted.
-Is the extraction of wisdom teeth different from normal tooth extraction?
There is no difference in the extraction of visible wisdom teeth from other tooth extractions. However, surgical extraction may be required for impacted wisdom teeth.
-What should I pay attention to after tooth extraction?
Do not consume food after tooth extraction until the effect of anesthesia wears off. Apply cold compresses (ice) at five-minute intervals for the first 24 hours to reduce pain and swelling. Do not spit, vacuum or gargle for the first 24 hours in order to prevent clotting and increase bleeding. Use the medicines prescribed by your doctor. Avoid very hot, spicy, acidic and grainy foods. There may be sutures(stitches) in the mouth, be careful to keep the sutures clean and not to accumulate food on it. Avoid excessive lip and tongue movements to avoid damaging the sutures. Do not consume cigarettes or alcohol during the recovery period.
-What are the emergencies that I need to consult a doctor after tooth extraction?
Mild swelling on the face, bleeding in the form of leakage, pain that decreases after taking painkillers, and jaw limitation are normal after extraction. However, if there is excessive bleeding that does not go away with pressure, swelling that lasts for more than a few days, numbness or tingling in the jaws, the doctor should be contacted.
2—Dişeti çekilmesi nedir?
Sağlıklı dişeti, dişi sıkıca sararak dişi dış etkenlerden korur. Ancak, bazı durumlarda dişeti geriye giderek kök yüzeyi açığa çıkabilir. Dişeti çekilmesi herkeste oluşmadığı gibi hemen fark edilmeyebilir.
-Dişeti çekilmesi belirtileri nedir?
Açığa çıkan kök yüzeyinde sıcak-soğuk hassasiyetleri, fırçalarken gözlenen kanama, kızarıklık ve şişlik, dişin normalden daha uzun görünmesi, özellikle sert yiyecekler yerken kanama dişeti çekilmesi belirtilerindendir.
-Dişeti çekilmesi neden olur?
Hijyen eksikliğine bağlı aşırı diştaşı birikimi,
Yanlış fırçalama yapmak,
Çok sert diş fırçası kullanmak,
Dişlerde çapraşıklık,
Dudak bağının(frenilum) uzun olması,
Vitamin eksikliği,
Dişetinin ince oluşu,
Diş sıkma,
Yaşlılık,
Genetik yatkınlık,
Hormonal değişimler ve çeşitli hastalıklar çekilmeye sebep olabilir.
-Dişeti çekilmesi tedavisi nasıl olur? Kendiliğinden düzelir mi? Evde kullanabileceğim bitkisel bir tedavi veya ilaç var mıdır?
Maalesef dişeti çekilmeleri kendiliğinden geçmez. Ayrıca bitkisel tedavi veya ilaçla dişeti kendi kendine tekrar yükselmez. Profesyonel bir müdahale şarttır. Dişeti çekilmelerinde tedavi, öncelikle nedenin ortadan kaldırılması, hijyenin ideal hale getirilmesi ve diştaşı temizliğidir. Gerektiğinde daha sonra cerrahi müdahaleye geçilir. Dişeti çekilmelerinde, sıklıkla damaktan alınan dişeti nakli ameliyatları yapılmaktadır.
-Tedavi sonrası iyileşme nasıl gerçekleşir?
Dişeti nakli olsun veya olmasın ameliyatla tedavi edildiğinde ağız içinde dikişler vardır. Yara bölgesinin iyileşmesi 10-14 gün kadar sürer. Bu süreçte hastanın ilaçlarını düzenli kullanması, yara bölgesinin temizliğine ve dikişlerin düşmemesine dikkat etmesi istenir. Nakil sürecinde, travmadan kaçınılması ve sigara kullanılmaması damarlanmanın sağlanması ve naklin başarısı için çok önemlidir. Naklin başarısı ilk haftada belli olsa da dokunun tamamen iyileşmesi 3-6 ay kadar sürer.
-Aynı bölgede tekrar dişeti çekilmesi olur mu?
Damaktan alınan dişeti daha kalın ve sert yapıdadır. Nakil olduğu bölgede dişeti dişi sıkıca sarar ve tekrar çekilmeye karşı dirençli olur.
-Dişeti çekilmesi nasıl önlenir?
Dişeti çekilmesini önlemenin en kolay yolu, orta-yumuşak fırça kullanarak dişetine çok baskı uygulamadan olarak fırçalamak, düzenli diş hekimi kontrolünde olmak, diştaşı temizliğinin belirli aralıklarla yapılmasına dikkat etmektir.
—-İngilizcesi
-What is gingival recession?
Healthy gingiva adheres tightly to the tooth and protects it from external factors. However, in some cases, the root surface may be exposed by receding the gingiva. Gingival recession does not occur in everyone and may not be noticed immediately.
-What are the symptoms of gingival recession?
Hot-cold sensitivities on the exposed root surface, bleeding while brushing, gingival redness and swelling, the appearance of the tooth longer than normal, bleeding especially when eating hard foods are the symptoms of gingival recession.
-What causes gingival recession?
Excessive calculus accumulation due to lack of hygiene,
Wrong brushing
Using a very hard toothbrush
Crowding in the teeth,
Long lip tie (frenilum)
Vitamin deficiency
Thin gingiva,
bruxism,
Senile,
Genetic predisposition,
Hormonal changes and various diseases can cause gingival recession.
-How is gingival recession treated? Will it heal naturally? Is there any herbal treatment or medicine that I can use at home?
Unfortunately, gingival recessions do not go away on their own. In addition, the gingiva does not rise again on its own with herbal treatment or medicine. Professional intervention is essential. Treatment in gingival recessions is primarily to eliminate the cause, to optimize hygiene and to clean the calculus. If necessary, then surgical intervention is started. In gingival recessions, gingival transplant surgery is often performed.
-How does recovery take place after treatment?
There are stitches(sutures) in the mouth when treated with surgery, with or without a gingival transplant. It takes 10-14 days for the wound area to heal. In this process, the patient is asked to use their medications regularly, to pay attention to the cleanliness of the wound area and to ensure that the stitches(sutures) do not fall. Avoiding trauma and not smoking during the transplant process are very important for vascularization and the success of the transplant. Although the success of the transplant is evident in the first week, it takes 3-6 months for the tissue to heal completely.
-Will there be gingival recession in the same area?
The gingiva taken from the palate is thicker and harder. In the transplant area, the gingiva tightly surrounds the tooth and becomes resistant to gingival recession.
-How to prevent gingival recession?
The easiest way to prevent gingival recession is to brush without applying too much pressure to the gingiva using a medium-soft brush, to be under regular dentist control, and to pay attention to the cleaning of calculus at regular intervals.
3–Dişeti hastalığı nedir? Belirtileri nedir?
Sağlıklı dişeti pembe renkli, sıkı yapılı ve portakal kabuğu görünümündedir. Dişler üzerinde bıçak sırtı şeklinde sonlanır. Dişler üzerinde biriken diş plağı arttıkça, plak içerisinde bulunan çeşitli mikroorganizmalar periodontal hastalıkları oluşturmaya başlar. Periodontitis(İleri dişeti hastalığı), dişeti iltihabı ile birlikte çene kemiğinde de yıkımı yapan bir hastalıktır. Dişetlerinde kendiliğinden kanama, kızarıklık, ödem, renk değişikliği gibi hastalık semptomları gözlenir. Diş hekimi muayenesinde ise röntgende kemik kaybı görülür
-Dişeti hastalığı neden olur?
Periodontitisin(İleri dişeti hastalığı) ana sebebi diş taşı ve diş plağıdır. Ancak herkeste ilerleyen derecede hastalık gözlenmez. Çünkü hastalığın oluşumunda bir çok kolaylaştırıcı faktör bulunmaktadır. Diyabet(şeker hastalığı), osteoporoz(kemik erimesi), kanser gibi sistemik hastalıklar, yanlış fırçalama, vitamin eksikliği, sigara kullanımı gibi çevresel faktörler ve genetik yatkınlık önemlidir.
-Diş eti hastalığı nasıl tedavi edilir?
Dişeti sağlığının geri kazanılması için ağız hijyeninin sağlanması şarttır. Derin diş taşı temizliği, iltihaplı dişeti dokularının uzaklaştırılması ve kök yüzeylerinin pürüzsüzleştirilmesi gerekir. Ayrıca hastalığın ilerlemesine sebep olan kolaylaştırıcı faktörlerin azaltılması için tıbbi kontrol ve ilaç düzenlemeleri gerekebilir.
-Dişeti hastalığı tedavi edilmediğinde nelerle karşılaşırım?
Dişeti hastalıkları tedavi edilmezse, enfeksiyon çene kemiğinde yıkıma sebep olarak dişte ağrı, sallanma, devrilme ve sonuçta diş kaybına sebep olur.
-Dişeti hastalıkları önlenmesi için neler yapılabilir?
Profesyonel diş taşı temizliğinin ardından düzenli fırçalama, genel sağlığa dikkat etmek, ağız içi travmalardan kaçınmak, sigara kullanımını bırakmak, stresten uzak durmak, beslenme düzenine dikkat etmek dişeti hastalıklarının önlenmesinde etkilidir.
—İngilizcesi
-What is gum disease? What are the symptoms?
Healthy gingiva has a pink color, tight structure and orange peel appearance. It ends in the form of a knife-edge on the teeth. As the dental plaque accumulates on the teeth increases, various microorganisms in the plaque begin to form periodontal diseases. Periodontitis (Advanced gingival disease) is a disease that destroys the jawbone along with gingivitis. Disease symptoms such as spontaneous bleeding, redness, edema, and discoloration are observed in the gums. In the dentist examination, bone loss is seen on the x-ray.
-What causes gum disease?
The main cause of periodontitis (advanced gum disease) is tartar and dental plaque. However, not everyone has a progressive disease. Because there are many facilitating factors in the formation of the disease. Systemic diseases such as diabetes, osteoporosis , cancer, environmental factors such as wrong brushing, vitamin deficiency, smoking and genetic predisposition are important.
-How is gum disease treated?
Oral hygiene is essential for restoring gingival health. Deep calculus cleaning, removal of inflamed gingival tissues and smoothing of root surfaces are required. In addition, medical control and drug regulation may be required to reduce the facilitating factors that cause the progression of the disease.
-What happens if gum disease is not treated?
If gingival diseases are not treated, the infection causes destruction of the jawbone, causing pain, shaking, tipping and eventually tooth loss.
-What can be done to prevent gum diseases?
Regular brushing after professional scaling, paying attention to general health, avoiding intraoral trauma, quitting smoking, avoiding stress, paying attention to diet are effective in preventing gum diseases.
İyi Günler